WireGuard setup Openwrt with VXLAN
Using the latest openWRT/LEDE image (openwrt-21.02.0-rc3-x86-generic-generic-ext4-combined) for WireGuard on GNS3. By default we must to change Openwrt network IP(192.168.100.1 and 192.168.100.2), GW (192.168.100.254) and add DNS (8.8.8.8):
Also change DNS settings to 8.8.8.8 :
For WireGuard we must install following packages (the same thing can be done in GUI "System" --> "Software" section).
opkg install luci-proto-wireguard wireguard-tools luci-app-wireguard kmod-wireguard
Initial setup of Wireguard is privarte and publick key generation on both nodes and setup via luci interface
mkdir /VPN
cd /VPN
#Generating public key
wg genkey > pub.key
#Generating private key
wg pubkey < pub.key > pri.key
After generating private and public keys we must setup WireGuard via luci (WebGUI) inteface by creating new network interface "Add new Interface..." in Network --> Interface.
The configuration on Node 192.168.100.2
First we must create WireGuard interface, the name of interface is wg0:
After it we setup new interface be defining, "Private Key", which was generated in last step, also good idea to setup Listen Port (exp 51820) and the IP of the Wiregaud interface (10.0.0.2/24) on the node OPENWRT_192.168.100.2, on OPENWRT_192.168.100.1 we will use 10.0.0.1/24And setting for remote node the following fields:
Description : 192.168.100.2
Public Key: ENleaCdfs - the file pub.key in other node (OPENWRT_192.168.100.1)
Allowed IPs: 10.0.0.0/24
Endpoint Host: 192.168.100.2
Endpoint Port: 51820
Persistent Keep Alive: 10 - optional settings, this will help work from behind the NAT and also tunnel will be up fro all time.
The same configuration must be applied to other node. To activate the change or after modification you need to restart network service in menu "System" --> "Startup".
To check status status of WireGuard from CLI is just ping the remote node to use the wg comand to see the status of tunnel. The bad thing that you will not see any active socket open in netstat -nap command.
The same info can be seen from GUI in "Status" --> "WireGuard" menu section.
If tunnel is down (transfer is none) or the remote node does not respond to ping or always good to check the wireshark on GNS3 or tcpdump on node also to see in wg if the remote public key matches local peer key. Also to see if the network node you are pinging is in routing table. The bad thing that you will not see any active socket open in netstat -nap command.
VXLAN configuration
To set up the L2 connectivity from one node to other we will use vxlan, it's an encapsulation technique to encapsulate OSI layer 2 Ethernet frames in layer 4 UDP datagrams (RFC4789).
For it we will need to install following packages:
opkg install vxlan kmod-vxlan luci-proto-vxlan
After installing the needed packages we will have to create net network interface "Add new interface..." in "Network" --> "Interfaces". As we are running IPv4 network we use the VXLAN (RFC7348) interface type.
Also for first/testing we setup the VXLAN interface binding on LAN interface, in this case the traffic will not be encrypted, the configuration should be as follows:
Like in WireGuard configuration VX0 interface should be added to Firewall-zone: lan, to allow full access for testing.
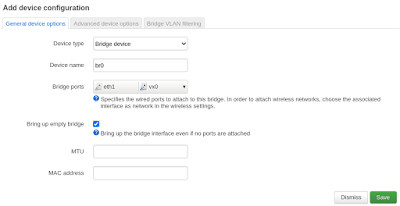
To test IP connectivity we will create new BRIDGE interface with IP. The new Bridge will connect VX0 interfaces to LAN intefaces eth1.
In OpenWRT new bvridge interface is create in Network --> Interfaces --> Device "Add device configuration"
And after it create IP interface in "Interfaces" section and assign IP address on 172.16.0.1 on left node and 172.16.0.2 on right node.
At this point the IP connectivity should be working after restarting network service or after reboot, the issue with vxlan as in WireGuard, the netstat does not show socket usage. So classically only Wireshark or TCP dump can show VXLAN traffic:
The configuration of the VXLAN interface vx0 in OpenWRT:
And ofcource the tcpdumo traffic sniff on vx0 intergface to see if our traffic can pass the new WireGuard and VXLAN tunnels:
The main disadvantage (nasty thing) is that the MTU/frame size must be bellow MTU of the vx0 interface (in our case less then 1370 Bytes), also including the Ethernet and vlan headers. So setting the network we must set the PC1 and PC2 MTU size much smaller, also keeping in mind that we could be using QinQ or other encapsulation methods.
A topic for L2 fragmentation i think:)





















No comments:
Post a Comment